|
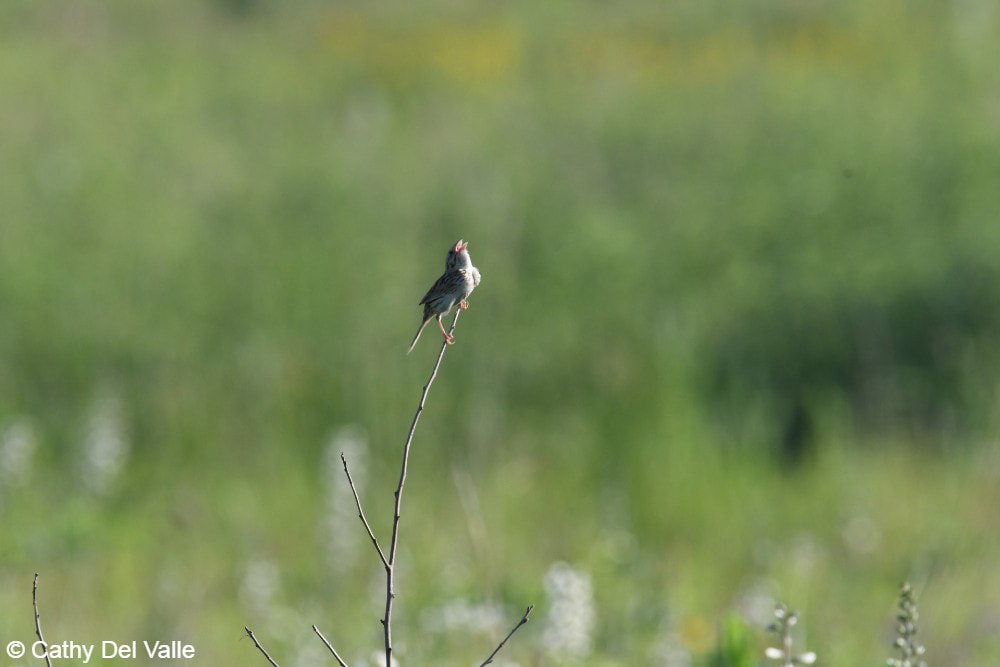
By Antonio Del Valle MS Student  Sunrises over the tallgrass praire were a wondrous daily event to behold while surveying at Nachusa Grasslands. This summer, as part of my graduate research project at Northern Illinois University, I had the opportunity of studying some of the many bird species that call Nachusa Grasslands home. Luckily, surveying birds is an activity that you can do by yourself, which was a key factor in being able to safely conduct my research project in the midst of a global pandemic. The focus of my research is to determine how birds that breed on the prairie are impacted by some of the large scale disturbances on the prairie landscape—mainly bison herbivory and prescribed fire. Different bird species prefer different types of prairie. Species such as killdeer (Charadrius vociferous) and upland sandpiper (Bartramia longicauda) prefer shorter prairies that, at Nachusa, are maintained through the eating of plants by bison and frequent prescribed fires. In contrast, species such as Henslow’s sparrow (Centronyx henslowii) and sedge wren (Cistothorus platensis) prefer dense, tall prairies that are maintained through infrequent disturbances.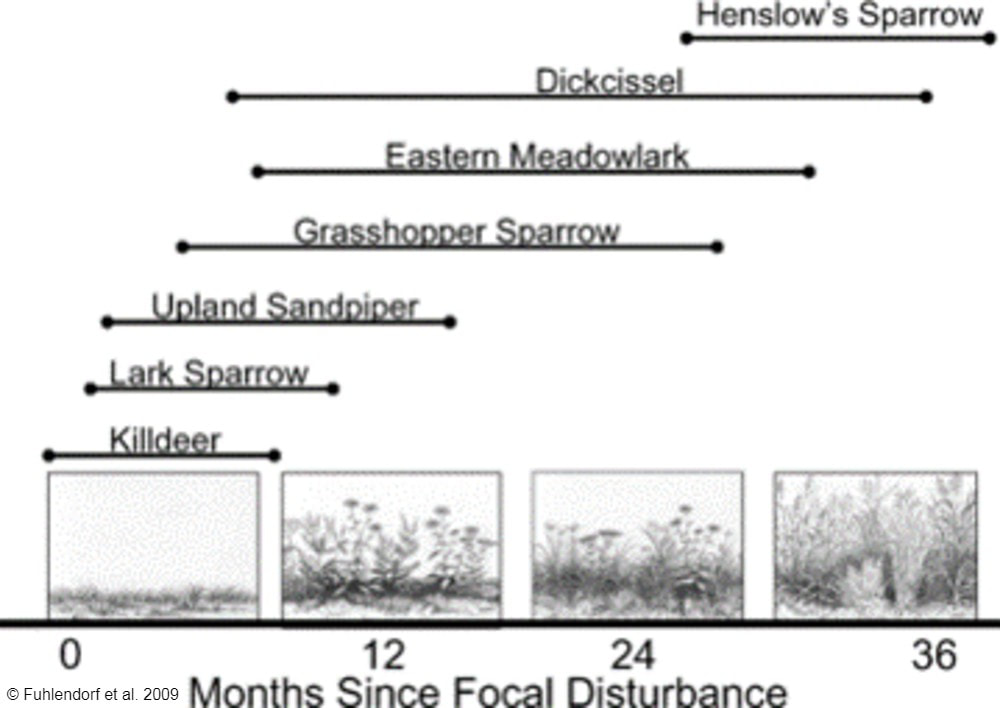  A figure describing the relationship between different grassland bird species presence and months since a disturbance event has occurred on the prairie. Grassland birds are a suite of species that specialize in using prairie habitat as their preferred place to breed and raise young. These species are of particular interest to me because grassland birds have experienced drastic population declines. A recent paper published in Science shows just how serious this decline has been. 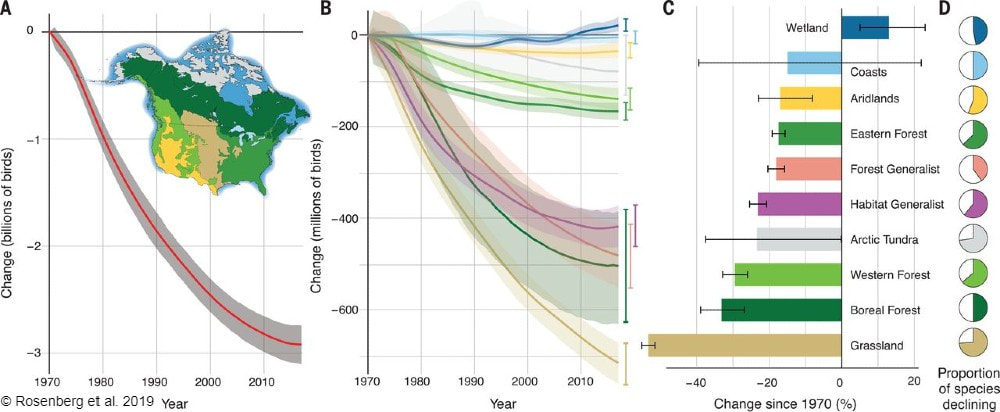 Bird populations in North America have declined by three billion individuals since 1970. Grassland birds in particular have declined more than any other group of birds. But it is not all doom and gloom for these grassland birds. Thanks to the hard work put into the restoration, management, and conservation of the tallgrass prairie habitat at Nachusa Grasslands, there are bountiful places for these types of birds to breed during the summer. My research aims to help us understand more about these declining species. Preserves such as Nachusa Grasslands give me an opportunity to observe them in areas where they are still relatively prevalent.  High quality prairie restorations take a lot of hard work but provide great habitat for many declining and rare plants and animals. A typical morning of surveying birds starts out by waking up well before sunrise. I set my schedule to arrive to Nachusa around 5:30 AM in order to start surveying during peak bird activity. Coming prepared with coffee and waterproof clothes were key factors in staying awake and dry while traversing the dew-soaked prairie. Upon arriving to a survey point at the preserve, I begin surveying birds via sight with my binoculars, as well as by sound. I record all of the birds I see and hear into my field notepad for five minutes. While surveying, I record the number of individuals of each species, estimate their distance from me, and record any breeding behaviors that are displayed. Surveying in this systematic fashion allows me to look at the data later and compare what birds were seen in what areas, how many were present, and whether I can confirm that they were breeding (according to eBird’s breeding bird behavior codes). Additionally, this format allows me to compare my data to other data sets across different years and potentially different preserves/sites.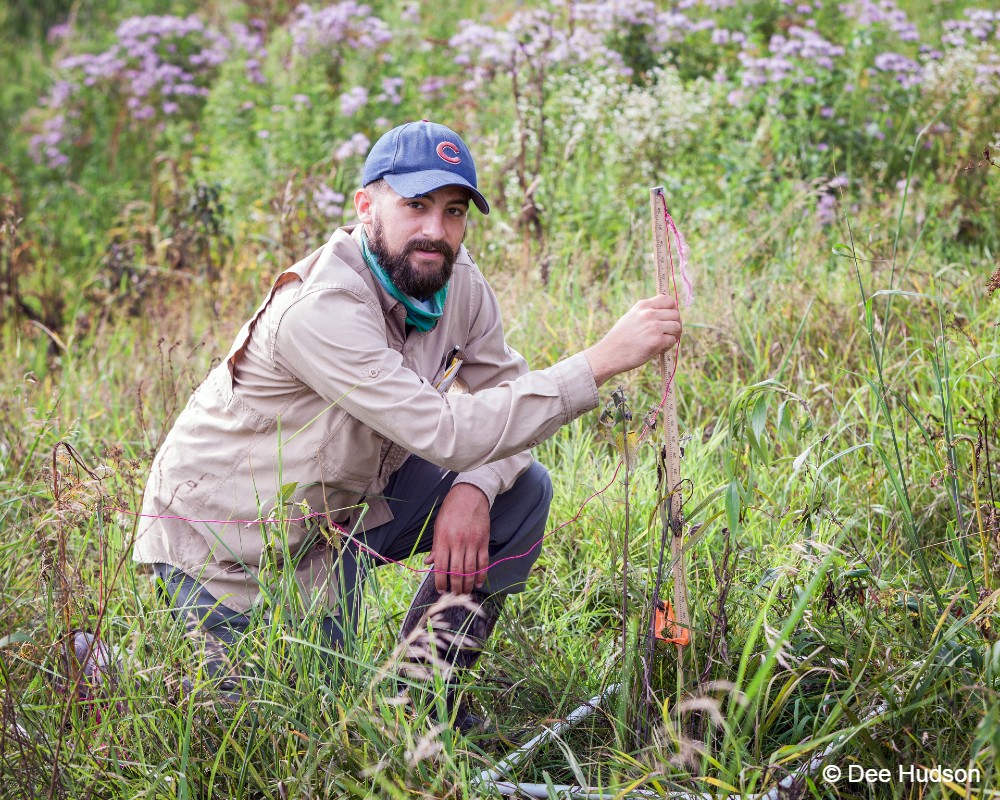  The depth of the thatch layer covering the ground is measured by using a ruler. This layer of dead plant material is important for certain species that require cover. In addition to surveying birds, I also survey vegetation and bison density through dung counts. Vegetation surveys involve measuring vegetation height, thickness of thatch layer, and percent cover of plant species. These measurements give me quantitative values to describe the vegetation structure within different areas of the preserve. Bison density is calculated through systematically counting units of dung at my survey locations. Looking at bison density in different areas of the preserve can help show where bison are spending most of their time (and eating more plants). One of my favorite birds to observe this summer was the Henslow’s sparrow. This secretive sparrow is rarely seen on the prairie, as it spends most of its summer down low in the grasses and only pops up once in a while when singing or flying. The Henslow’s sparrow song is unique as well. Cornell University’s All About Birds online field guide describes it as the simplest and shortest song of any North American bird, and to me it sounds like a faint hiccup. These sparrows have a greenish wash on their face and fine streaks on their flanks, which help to distinguish them visually from other sparrow species if you have the pleasure of catching a glimpse of them. They, along with many of the other grassland breeding birds, are now on their way back to their overwintering grounds in Central and South America. The prairies will be noticeably quieter until they begin to return in the spring again. I’m looking forward to analyzing the data collected this summer and preparing for next year’s field season over the next few months. I hope that my research can help provide knowledge to aid in the continued conservation of these grassland bird species. Nachusa Grasslands is a wonderful place to observe these birds and many other plants and animals in their native habitat. Citations & Resources: Fuhlendorf, S.D., et al. (2009). Pyric herbivory: Rewilding landscapes through the recoupling of fire and grazing. Conservation Biology 23:588–598. Rosenberg, K.V., et al. (2019). Decline of the North American Avifauna. Science 366(6461):120-124. Tony’s ongoing graduate research is supported by the following sources:
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Blog CoordinatorDee Hudson
I am a nature photographer, a freelance graphic designer, and steward at Nachusa's Thelma Carpenter Prairie. I have taken photos for Nachusa since 2012. EditorJames Higby
I have been a high school French teacher, registered piano technician, and librarian. In retirement I am a volunteer historian at Lee County Historical and Genealogical Society. Categories
All
Archives
January 2024
|
CONNECT WITH US |
|



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed